In the Goldilocks region of our galaxy, NASA’s Kepler Space Telescope found an Earth-like planet orbiting a nearby star. Almost 500 light-years away from Earth, in the Cygnus constellation, is Kepler-186f. The region surrounding a star where planetary-mass objects with sufficient atmospheric pressure can support liquid water on their surfaces is known as the habitable zone, sometimes known as the Goldilocks zone.
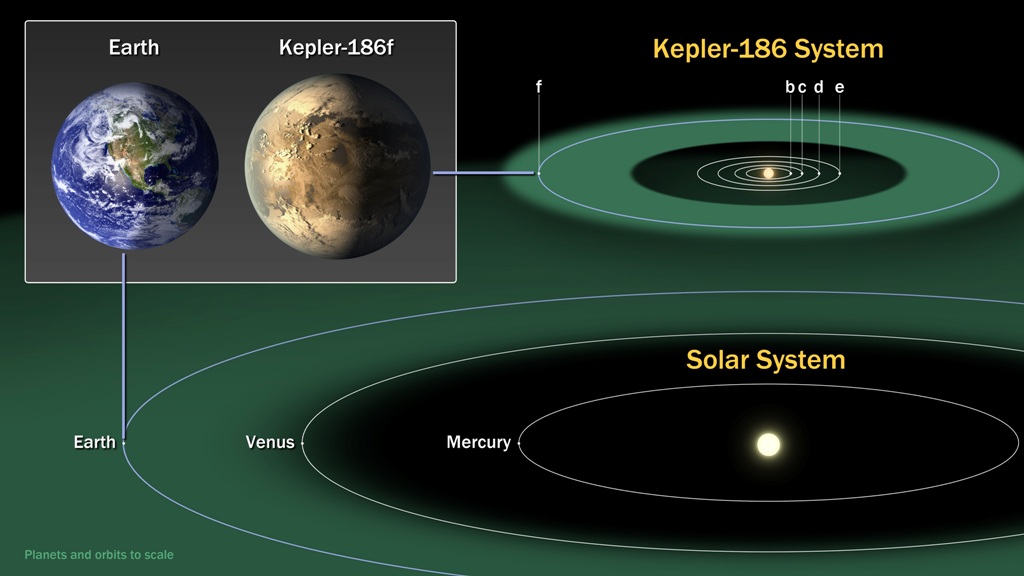
Although it has been estimated that there are at least 40 billion Earth-sized planets in our Milky Way Galaxy, this particular discovery is the first of its kind to be located near a star’s habitable zone.
The Kepler-186f system contains Kepler-186f and 4 other planets that orbit a neighboring star. This suggests that the probability of life on this planet exponentially increases if the star that orbits it is similar to our Sun.
“We are aware of only one planet, Earth, where life exists. Elisa Quintana, a research scientist at NASA’s Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, Calif., and the paper’s primary author, stated that while searching for extraterrestrial life, they focus on finding planets with characteristics that resemble those of Earth. A significant advance is the discovery of a planet in the habitable zone that is roughly the size of Earth.

Kepler-186f’s nearby star is only receiving one-third of the energy that our Sun provides despite having half the mass and size of our Sun. One rotation of Kepler-186f’s star occurs every 130 days.






