In the last decade, the number of people adopting a vegetarian or vegan based diet has skyrocketed. The reasoning behind these dietary changes stem from ethical, environmental and personal health concerns.
In the UK, veganism has seen a 350% rise in popularity in the last decade, with around 542,000 brits adopting a meat and animal product-free diet. This rise in vegan and vegetarian based diets has been primarily attributed to the younger generation, with 20% of 16- to 24-year-olds in the UK following a vegetarian diet.
“Young people have increased their awareness of the environmental impact of eating meat from 8% in 2007 to 40% in 2013,” said the Vegetarian Society. In light of this monumental societal change, Michelle McMacken, a board-certified internal medicine physician and an assistant professor of medicine at NYU School of Medicine and an enthusiastic supporter of plant-based nutrition, put together a list of the 7 things that happen when you give up meat. Inspired by McMacken’s article, we have compiled a similar list detailing 8 things that happen when you adopt a meat-free diet.
Personal Health

1) Greatly Reduces Your Chances Of Getting Type 2 Diabetes
Studies have shown that a diet containing animal protein, especially red and processed meat, significantly increases the risk of type 2 diabetes. In a study, set out to compare the diabetes rates of vegans and members of the Adventist Mortality Study and Adventist Health Study, the Adventist population have doubled the rate of diabetes. In addition, the study also found that in this population, eating meat once or more a week over a 17-year period increased the risk of diabetes by 74 percent.
Animal fat, animal-based (heme) iron, and nitrate preservatives are believed to be responsible for this increased risk. Studies have shown that they damage pancreatic cells, worsen inflammation, cause weight gain, and impair the way our insulin functions. As a result, it is believed that adopting a meat-free diet would significantly reduce the risk of getting type 2 diabetes, and could even improve or help reverse diabetes in those who have already been diagnosed. Today, it is estimated that around 38 percent of Americans are pre-diabetic.

2) You’ll get the right amount—and the right type—of protein.
Protein is usually an omnivore’s first line of defense when their meat-filled diet is questioned; however, if you are meeting your daily calorie needs, you will get all the protein you need from a plant-based diet.
In the US, omnivores get more than 1.5 times the optimal amount of protein. While many believe that eating an excess amount of protein – especially from meat – will make them stronger and leaner, in reality the opposite occurs.
Excess protein is stored as fat or turned into waste, leading to weight gain, heart disease, diabetes, inflammation and cancer in many individuals that consume too much protein on a regular basis. In comparison, protein contained in whole plant foods has been linked to disease prevention. Michelle McMacken explains:
“[T]he protein found in whole plant foods protects us from many chronic diseases. There is no need to track protein intake or use protein supplements with plant-based diets; if you are meeting your daily calorie needs, you will get plenty of protein. The longest-lived people on Earth, those living in the “Blue Zones,” get about 10% of their calories from protein, compared with the U.S. average of 15-20%.”

3) Reduce Inflammation In Your Body
Meat, cheese and other processed foods have been linked to elevated levels of inflamation in the body, which can lead to a number of severe long-term medical conditions, including the development of atherosclerosis, heart attacks, strokes, diabetes and autoimmune diseases, among other conditions.
However, studies have show that when an individual switches to a plant-based diet, it can dramatically lower their level of C-reactive protein (CRP), an indicator of inflammation in the body. Plant-based foods are high in fiber, antioxidants, and other phytonutrients, making plant-based diets naturally anti-inflammatory.

4) Lower Blood Cholesterol
Studies have found that adopting a plant-based diet can lower blood cholesterol levels by up to 35 percent. In fact, going plant-based is said to have decreased blood cholesterol levels at the same rate as drug therapy, in many cases. Elevated blood cholesterol levels lead to atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of heart disease and strokes – two of the leading killers in the United States.
Michelle McMacken explains:
“Whole-food, plant-based diets reduce blood cholesterol because they tend to be very low in saturated fat and they contain zero cholesterol. Moreover, plant-based diets are high in fibre, which further reduces blood cholesterol levels. Soy has also been shown to play a role in lowering cholesterol, for those who choose to include it.”

5) Makes You Live Longer By Changing Your Genes
Environmental and lifestyle factors can switch genes on and off, which can help us live longer and healthier lives, according to a recent study. For example, a plant-based diet can decrease the expression of cancer genes in men with low-risk prostate cancer, according to recent findings.
In addition, plant-based diet are known to lengthen our telomeres, which are caps at the end of DNA chromosomes that work to keep our DNA stable. This suggests that our cells and tissue age more slowly, making us less prone to age-related diseases.
6) Gives Your Gut A Makeover
The microbiome, which is made up of trillions of microorganisms, produces critical nutrients, keeps our gut tissues healthy, protects us from cancer, turns genes on and off. Plant foods, especially those with a high fiber content, help shape a healthy microbiome by promoting the growth of friendly bacteria.
Michelle McMacken explains: “Landmark studies have shown that when omnivores eat choline or carnitine (found in meat, poultry, seafood, eggs, and dairy), gut bacteria make a substance that is converted by our liver to a toxic product called TMAO. TMAO leads to worsening cholesterol plaques in our blood vessels and escalates the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Interestingly, people eating plant-based diets make little or no TMAO after a meat-containing meal, because they have a totally different gut microbiome. It takes only a few days for our gut bacterial patterns to change – the benefits of a plant-based diet start quickly!”
Environmental and Ethical Concerns
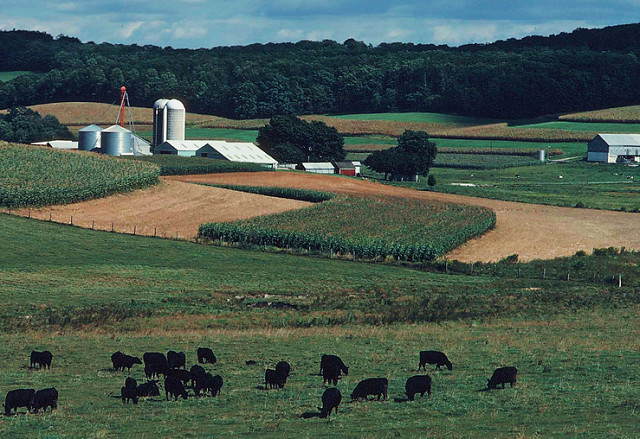

7) You Will Help Save The Environment
Animal agriculture – the single largest contributor to greenhouse gas emissions – contributes to 51 percent of the world’s greenhouse gas emissions. In addition, animal agriculture is also the leading cause of deforestation, species extinction and land and water use. In fact, 40 percent of the world’s land surface is used to feed the global population. However, the vast majority of this land – as much as 30 percent of the world’s total ice-free surface – is used to feed livestock.
In order to grow these crops, a large amount of fresh water is regularly required. In fact, one-third of the world’s fresh water is used to sustain global livestock production – which includes meat, milk and eggs. In addition to straining our limited land-based resources, the oceans are also suffering the effects of animal agriculture. Overfishing is rapidly depleting the oceans, causing detrimental effects of ecosystems vital to our own survival. It is estimated that the oceans may be fishless by as early as 2048.
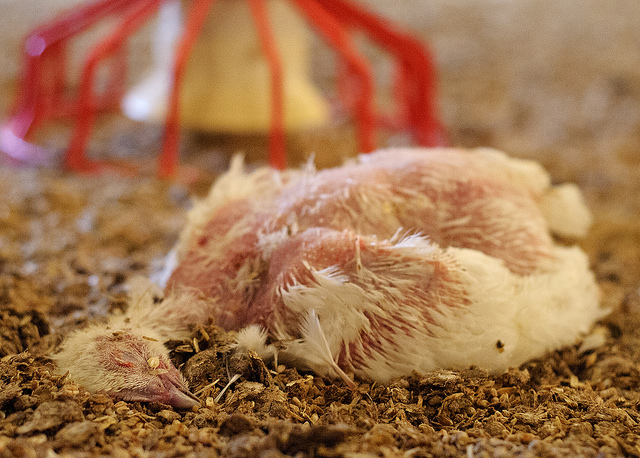

8) You Will Stop Promoting Animal Cruelty
Despite what many of us would like to believe about livestock production – cows, pigs, chickens all roaming around freely in an open field – the reality of the industry is another matter entirely. The majority of animals livestock production industry are raised in factory farms, the fastest growing method of animal production worldwide.
Animals raised in this environment are exposed to squalid and overcrowded conditions, poor treatment and inhuman practices. As a result, the animals living in these conditions become extremely unhealthy – both physically and mentally – which promotes stress, aggression and the spread of disease.






